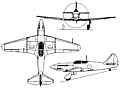
Late in 1942, work was well advanced at the MiG
bureau on several aircraft in parallel and referred to as
Series "A" prototypes, with which the OKB hoped to
fulfil a VP (vysotny perekhvatchik, or high-altitude
interceptor) requirement raised earlier in the year. The
first of these, the I-220, owed little or nothing to earlier
MiG fighters and was of mixed construction, the fuselage
being of metal forward of the cockpit and a
wooden monocoque aft, and the wings making use of
steel main and auxiliary spars with spruce outer panel
ribs. The first prototype, which was rolled out of the factory
in June 1943 and was first flown during the following
month, was initially powered with a low-altitude
Mikulin AM-38F engine of 1700hp. Armed with two
synchronised 20mm ShVAK cannon, the AM-38Fpowered
I-220 achieved speeds of 572km/h
at sea level and 630km/h at 7000m, practical ceiling being 9500m.
The prototype was then re-engined with a medium-altitude
AM-39 affording 1800hp for take-off and flown
in January 1944, flight testing continuing until the following
August. A second prototype also powered by
the AM-39 flew in September 1944, but differed in
armament, being the first Soviet fighter to carry four
20mm ShVAK cannon. The following data relate to the
second prototype.
The second Series "A" high-altitude fighter and referred to as the 2A, the I-221 was the first of the
OKB's fighter prototypes to be fitted with turbo-superchargers.
The I-221 was fitted with an AM-39A engine
rated at 1700hp for take-off and equipped with a centrifugal
compressor and paired TsIAM-developed
TK-2B turbo-superchargers which, it was anticipated,
would permit maximum power to be maintained to an
altitude of 13000m. Although adhering
closely in most other respects to the preceding I-220,
the I-221 had a rear fuselage of dural construction
rather than a wooden monocoque, and the outer wing
panels were extended, increasing span by a total of 2.00m. Armament consisted of two synchronised
20mm cannon. The initial flight test took place
on 2 December 1943, but the programme came to an
abrupt end when, during one of the prototype's early
trials, a piston rod fractured, the engine seized and the
aircraft crashed.