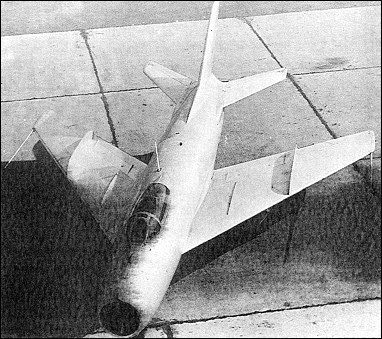
|
| During 1953, the MiG OKB launched the design of a
single-engined tactical fighter which was to utilise a
wing fundamentally similar to that of the twin-engined
SM-9, forerunner of the MiG-19, work on which was
proceeding in parallel. Officially designated I-370 and
assigned the OKB appellation of I-1, the new fighter received
a Klimov VK-7 turbojet rated at 3525kg and boosted to 5235kg with
afterburning. The prototype was flown for the first time
on 16 February 1955, but high speed performance
proved disappointing. It was therefore returned to the
factory where an uprated VK-7 engine was installed,
this having normal maximum and afterburning thrust
ratings of 3935kg and 6270kg respectively.
With a new wing, the quarter-chord sweepback
of which was increased from 55 to 57 deg, the prototype
was redesignated I-2 by the OKB. Limited
testing of the I-2 was undertaken during which design
maximum speed proved unobtainable. A further development
of the basic design, the I-3 (I-380), remained
unflown owing to the non-delivery of its more powerful
VK-3 engine.
| WEIGHTS |
| Take-off weight | 8300 kg | 18298 lb |
| Empty weight | 5086 kg | 11213 lb |
| DIMENSIONS |
| Wingspan | 9.00 m | 30 ft 6 in |
| Length | 12.70 m | 42 ft 8 in |
| Wing area | 25.00 m2 | 269.10 sq ft |
| PERFORMANCE |
| Max. speed | 1452 km/h | 902 mph |
| Ceiling | 17000 m | 55750 ft |
| Range w/max.fuel | 2500 km | 1553 miles |
| bombardier, e-mail, 24.05.2011 12:44 This aircraft was a variant of the MiG-19 powered by a centrifugal flow Klimov VK-7 engine.It performed well on trials but the axial flow engines were the future for supersonic aircraft so the I-370 was forgotten reply |
|
Do you have any comments?
|
| 
COMPANY
PROFILE
All the World's Rotorcraft
|