|
Tupolev Tu-21940 |  |
| BOMBER | Virtual Aircraft Museum / USSR / Russia / Tupolev |
 |
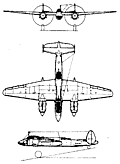
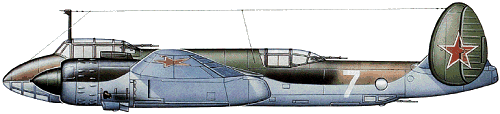
The origin of the Tupolev Tu-2 lay in the ANT-58, ANT-59 and ANT-60 light bomber prototypes that came from the design bureau of Andrei N. Tupolev during 1938-40; powered by two 1044kW Mikulin AM-37 V-12 engines, the ANT-58 made its first flight on 29 January 1941. The ANT-60 was re-engined with the big and powerful 1104kW M-82 radials because of the relative unreliability of the AM-37s. The result was the definitive Tu-2 bomber that was to see service with the V-VS during the last year of World War II and well into the 1950s. Soviet industry was still in a state of upheaval following the terrible years of 1941-2, when the German army struck deep into Belorussia and the Ukraine. The Tu-2 was too complicated an aircraft for the conditions prevailing, and after many months in which the Tu-2 was modified and simplified for the mass production lines, the Tu-2S (Seriinyi, or series) appeared, flying for the first time on 26 August 1943. A small number of Tu-2s had previously been passed to frontline regiments in September 1942, where their performance, armament and bombload had received general enthusiasm. By January 1944 the first production Tu-2 and Tu-2S bombers had been passed to the regiments of the V-VS, but it was not until June of that year that Tu-2s saw action on a large scale. The sector was the Karelian (Finnish) front in the north where the V-VS forces, under the overall command of General A.A. Novikov, numbered 757 aircraft of the 13th VA (Air Army), the V-VS KBF (Red Banner Baltic Fleet) and the 2nd GVIAK (guards fighter corps). Of the 249 Tu-2 and Petlyakov Pe-2 light bombers in the Soviet order of battle, many came under Colonel I.P. Skok's 334th Bomber Air Division which subseguently received a citation for its work. Reconnaissance work was now being carried out by Tu-2D and Tu-2R aircraft with modified mainplanes, nose glazing, and capacity for vertical and oblique cameras. Wartime production of the Tupolev Tu-2 and its sub-types amounted to 1,111. As a bomber it did not come into its own until the autumn of 1944. However, as German resistance stiffened on nearmg the eastern borders of the Reich V-VS bombers, including Tupolev Tu-2s, were called up to attack strongpoints at Kustrin, K?nigsberg and other fortified ports and cities. September 1945 saw many Tu-2s in action against the Japanese Kwantung Army in Manchuria before the final surrender.
|  COMPANY PROFILE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |

|