|
| The first prototype flew on July 1, 1939. Entered service in August 1941. A total of about 20000 aircraft were built

| MODEL | Fw 190D-9 |
| CREW | 1 |
| ENGINE | 1 x Junkers Jumo 213A-1, 1324kW |
| WEIGHTS |
| Take-off weight | 4840 kg | 10670 lb |
| Empty weight | 3490 kg | 7694 lb |
| DIMENSIONS |
| Wingspan | 10.5 m | 34 ft 5 in |
| Length | 10.2 m | 33 ft 6 in |
| Height | 3.35 m | 11 ft 0 in |
| Wing area | 18.3 m2 | 196.98 sq ft |
| PERFORMANCE |
| Max. speed | 685 km/h | 426 mph |
| Ceiling | 12000 m | 39350 ft |
| Range | 835 km | 519 miles |
| ARMAMENT | 2 x 20mm cannons, 2 x 13mm machine-guns, 1 x 500kg bomb |
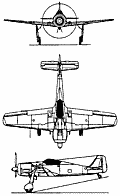 | A three-view drawing (1663 x 1213) |
| Aaron, e-mail, 06.09.2010 03:08 Ron,
I admit that I have not read any of Brown's books, so I can't make any judgement calls on them. I do know however, that you have to read test reports very carefully if you wish to compare apples to apples. A test of a F8F-1 unmodified aircraft climbed to 10,000ft. in 94 seconds (6383fpm. avg.). And a lightened P-51B-5 on 44-1 fuel was recorded as climbing at 4670fpm at 3,500ft. But these were isolated instances and not representitive of a fully loaded clean aircraft in the field of battle. I would really like to know the test weight and the amount of boost used on the FW-190D to get it to climb at 5000fpm. As I stated before I have seen the optimal climb rate of the FW-190D-9 in all up interceptor mode was about 4400fpm.
This was an excellent climb rate and definitely better than the Merlin powered Mustangs it met in combat. reply | | Ron, e-mail, 28.01.2010 09:32 360 deg turn for the A-5 with only 2 cn and 2 mg took around 21.5 sec. Interestingly that is right between the 3 gun and the 5 gun Bf 109G-2 (20.8 and 22.6 sec respectively).
Of course the La-5FN turned in around 18.5 sec. and the Yak-9D only took 16.5 roughly in a Soviet mock dogfight including the 6 gun Fw 190A-4 which did about 22.5 sec.
Those 2 Russian models were the most produced by the Soviets in the war. The most numerous models in the Luftwaffe were the Bf 109G-6 and the Fw 190A-8 with even slower turn performance! Therefore, most German pilots avoided horizontal turns in a duel. Was the extra firepower worth it? The average pilot was no longer the marksman required by a 3 gun Bf 109F. reply |
| Francis Maigné, e-mail, 22.12.2009 12:30 Fw 190 Fred
Avec le Bf 109, le Focke Wulf 190 sera le chasseur standard de la Luftwaffe pendant la Seconde Guerre Mondiale. L'idée d'utiliser un moteur en étoile sur un chasseur était hardie en Allemagne à l'époque. Le poids du moteur et la question de son refroidissement retardèrent le développement de l'avion.
Apparu près de 5 ans après le Messerchmitt, il lui est supérieur dans presque tous les compartiments de combat. Ce fut non seulement un chasseur exceptionnel, mais il pouvait également transporter des charges de bombes et fournir appui tactique fort apprécié.
Sa seule vrai faiblesse était le combat à haute altitude, là où croisaient les vagues de quadrimoteurs alliés qui attaquaient le coeur de l'Allemagne. Le Long Nez, apparu en 1944 et équipé de moteur en ligne remédiaient à cette faiblesse, mais la qualité décroissante des pilotes allemands et l'absolue supériorité numérique alliée annulèrent ses atouts techniques.
Description : Monomoteur de chasse et de chasse-bombardement, monoplace sous verrière monobloc s'ouvrant en coulissant vers l'arrière, monoplan voilure basse cantilever, mono dérive, empennage horizontal classique cantilever, train d'atterrissage classique escamotable vers l'intérieur dans l'épaisseur de l'intrados de la voilure, roulette de queue rétractable vers l'arrière. Construction entiére ment métallique, sauf les gouvernes de direction et de profondeur entoilées sur armature métal. 1 moteur tractif de 14 cylindres en dou ble étoile, hélice VDM tripale métallique à pas variable.
Fuselage : Formé de cadres et de lisses revêtus de métal, comportant à l'avant le moteur en étoile et son bâti fixé en partie sur la face avant du longeron principal de l'aile et sur la cloison pare-feu. Celle-ci suivie des instruments de la planche de bord et des comman des vol et moteur, dans un poste de pilotage recouvert d'une verrière aplatie à vision totale, moulée d'une seule pièce, coulissant sur le dos du fuselage, vers l'arrière. Les réservoirs de fuselage se trouvant à la partie inférieure sous l'habitacle, juste en arrière du longeron principal de voilure. La partie arrière du fuselage contenant les commandes rigides de vol ,bouteilles d'oxy gène, compas et coffret de
secours, se terminant par la dérive. L'extrémité arrière du fuselage contenant les dispositifs d'escamota ge et d'amortissement de la
roulette de queue portée par une fourche.
Voilure : De forme trapézoïdale, présentant un dièdre positif et des bords marginaux arrondis. Bi-longeron , construite d' une seule pièce, constituée d'un longeron principal traversant la partie basse du fuselage, et d'un longeron arrière par aile, fixé au cadre fort du fuselage se trouvant à l'aplomb de la partie avant de la verrière, de nervures pleines et de lisses perpendiculaires, le tout recouvert de panneaux de métal. La partie arrière occupée de volets coiffés par la partie supérieure du revêtement, et d'aile rons d'un seul tenant. Le train d'atterrissage étant fixé sur un tourillon sur la face avant du longeron principal. De grande lon gueur et à large voie, ce dernier procurant une excellente stabilité. Sa rétraction s'effectuant vers l'intérieur par variation de pres sion dans un circuit d'huile.
Empennages : Le plan stabilisateur, à incidence variable par commande mécanique rigide, composé de deux longerons: l'un prin cipal en cornière en I et un longeron avant de même forme, mais de plus faible section. Les gouvernes de profondeur et de direction, d'os sature métallique entoilées et munies d'un compensateur fixe. La gouverne de direction articulée sur la partie verticale arrière de la déri ve.
Train d'atterrissage : Voie: 3,50 m, Empattement : 7,00 m
Sa seule vrai faiblesse était le combat à haute altitude, là où croisaient les vagues de quadrimoteurs alliés qui attaquaient le coeur de l'Allemagne. Le Long Nez, apparu en 1944 et équipé de moteur en ligne remédiaient à cette faiblesse, mais la qualité décroissante des pilotes allemands et l'absolue supériorité numérique alliée annulèrent ses atouts techniques.
VERSIONS :
F 190 V-1 : Monomoteur de chasse et de chasse-bombardement, monoplace sous verrière, s'ouvrant en coulissant vers l'arrière, monoplan voilure basse cantilever droite, mono dérive, empennage horizontal classique cantilever, train d'atterrissage escamotable vers l'intérieur, roulette de queue semi-rétractable. Construction entiérement métallique, sauf les gouvernes de direction et de profondeur en toilées sur armature métallique. 1 moteur de 18cylindres en double étoile Bmw 139 de 1550 cv, hélice tripale métallique à pas variable VDM de 3,30 m de diamètre, grosse casserole d'hélice, E: 9,515 m, L: 8,80 m, H: 3,96 m, Voie du train: 3,50 m. 1er vol: 01 /06 /1939, par Hans Sander, 1er prototype, Werk Nr 0001, D-OPZE. FO+LY.
F 190 V-2 : .Semblable au V1 à q ... reply | | eliko, e-mail, 04.11.2009 13:06 FW-190 wasnt good turn fighter . Soviet fighters could easily overturn him . Also had bad climb rate , thats why german pilots usually dive to avoid 6 o'clock attack . Most soviet pilots said it easier to fight with FW than BF . Adil Quliev ( 20 kills ) had just 1 killed BF , other 19 was FW . reply |
|
| | paul scott, e-mail, 19.10.2009 02:32 Grateful for the 'tooled up' Spit to counter the butcher bird, but that's credit to the Spit's designers, for being able to upgade it in the first place - Bob Norton's right though, it took allied endeavour to counter it really, as we all know, the Mustnag's success was Anglo-American - right down to the Brits naming nearly every American warbird by an 'American' name (Mustang in point) other than just its designation number. reply | | Ronald, e-mail, 30.08.2009 08:56 Roll-rate for the Anton was 162 degrees /second (250 mph); 126 for the Dora (300 mph).
360 turn took 23 seconds for the A-4, down to 19 (sans wing guns?); 26 for later Antons; 22 for Dora-9. reply | | Ronald, e-mail, 24.08.2009 05:09 Dive red-line was 466 mph for the Anton-4. Later Fw 190s dive tested to 594 mph terminal velocity. reply | | BOB NORTON, 12.07.2009 10:58 The FW190 was one of the finest fighterplanes of the war, only a hand full of allied planes could match it, P-51B+ tepestV Yak3 but the spitfireIX was the first of these to start plucking feathers of the butcherbird. The RAF did not or the USAAF defeated the luffwaffe on thier owns, it was an ALLIED effort. reply | | d.jay, 11.07.2009 08:11 So the luftwaffe had got out of range of spitfires because it could not fight them so it left is army in France out numbered. Looks like they had already give up any vctory. reply | | Art Deco, 11.07.2009 03:49 It is odd that a Luftwaffe ace like Pips Priller is best remembered for his flight down the Normandy beach in his FW-190. There was only a handful of fighters left in France because the 8th AF was conducting a strategic bombing offensive on Germany, escorted by long range fighters, that required a response, unlike the short-ranged sorties with inconsequential targets, which was all the Spitfires were capable of reaching. Bombers were destroying Germany and Mustangs, not Spitfires, were enabling them. That's where the Luftwaffe was. reply | | d.jay, 11.07.2009 00:10 So what happend to the luftwaffe in northen France by D-Day the Merlin Mustang had only just enterd service by then and was too busy escorting bombers. reply | | Art Deco, 10.07.2009 21:35 Spit IX's didn't contain the threat, they only met it. the low level raids over England were met by the lash-up Spit XII with single stage Griffon and Typhoon. However, Spit V's continued to operate over France and in the Med theater long after. reply | | d.jay, 10.07.2009 20:47 It only had airsuperiority for 10 months when the Spit mk IX came out which was a mk V with a two stage Merlin. The mk VIIs and VIIIs where only bluilt in small numbers because the FW190 threat had been contained by "Jonny" Johnson and co in mk IXs in 1943, Even when the FW190 was up engined whith a Jumo 213 the spit already had the griffon. reply | | Ronald, e-mail, 22.06.2009 08:16 The Russians clocked the Dora-9 at 22 seconds for a banked full turn of 360 degrees (unboosted). They were not very impressed since their fighters were 3 or 4 seconds quicker.
Still, it was an improvement over the Anton radial (Fw 190A) at 26 seconds. reply | |
| | leo rudnicki, e-mail, 01.05.2009 01:50 After playing with another engine with ducted spinner, the FW-190a appeared out of nowhere two years later over France, completely blowing the Bond 007 myth. Many veteran Battle of Britain pilots died or spent the war at the Stalag Luft Hilton, ie; Dogsbody & Lucky Tuck. RAF reacted awkwardly with Spit IX superceding Spit VIII in development while Spit V production, while just made obsolete, outpaced all other models. Typhoon production was pushed to counter FW raids over Jolly Old. Development of FW-190 F&G models prioritized due to a lack of Stuka replacement. Big bombs with trimmed fins to fit on the belly rack, torpedoes mounted with raised tailwheel, too many factory and field mod kits to shake a stick at. Forward armored bomber destroyers with MK108's. Mistel combination with JU 88. Wide-track gear was easier on the inexperienced than the Me 109's Whoopie wheels. Engineering details abounded in cowling / cooling system, throttle and mixture controls etc. Perfomance trailed off higher up, Turbo engine failed. FW 190-D9 with Junkers Jumo 213 solved the altitude problem eventually although Tank wanted DB 603's, even later fitted to some Ta-152H's. Can't find much on decals but if you write "Dieses machinen ist nicht fur fingerpoken und mittengrabben" real small om tracing paper soaked in glue, it works for me. reply | | Joel Philippe, e-mail, 23.03.2009 23:32 The whole FW-190 "A" series line is missing here!It is the most produced ans active FW fighters during WWII. reply | | bao, e-mail, 30.11.2008 16:34 In the picture is type V reply | | Geir J. Valla, e-mail, 31.10.2008 21:01 Hello ! I\\ am retoring a BMW 801 D2 14 cyl. radial engine for FW 190. Do anyone have a manual for this motor ?
I like to by a copy. reply | | Charles, e-mail, 13.10.2008 20:53 Do you know of a source for nomenclature stenceling used on the FW-190 aircraft written in German. I am trying to reproduce decals for a 60 size FW-190 but can not fine any conerical decals with the nomenclature included. reply | | Ronald, e-mail, 24.09.2008 07:46 Climb rate: Anton-8 = 3,445 ft /min. 19,685 ft /9 min. 6 sec.
Dora-9 = 6,225 ft /min. 19,685 ft /7 min. 6 sec.
Once the pilots got over the fact that the new Dora-9 borrowed the engine from a bomber, they liked how it could out-run, out-turn and out fly the A series Fw 190 in the vertical plane, though it lost a bit of it's roll rate. Later it did even better boosted. Still it was best at low altitudes and meant as a stop gap until the new Ta 152 arrived. The Antons had more guns (6-10) for attacking bombers and the Doras (sans outboard wing guns) took on the escort fighters or covered jets that were landing. reply |
|
Do you have any comments?
|
| 
COMPANY
PROFILE
All the World's Rotorcraft
|




 eliko
eliko




Red Fleet article Nov '43 USAAF translation from Russian (Tactical and technical trends #36), a summary of one year of front wide encounters: "The FW-190A will INEVITABLY offer turning combat at a minimum speed" "FW-190A pilots do not like to fight in vertical maneuvers."
reply