|
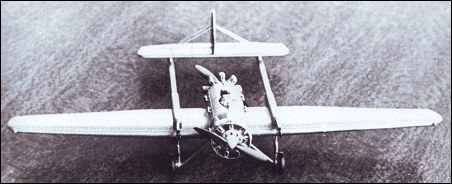
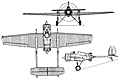
| Of unconventional design in employing a tandem fore-and-aft engine arrangement and twin tailbooms embodying recoilless gun tubes as integral, but non-load-carrying, structural components, the ANT-23 single-seat fighter was conceived at the AGOS TsAGI by Viktor N Chernyshov, one of Tupolev's brigade leaders. Of all-metal construction with smooth stressed skinning for the fuselage and wing - the latter and the tail surfaces being strengthened by externally-attached inverted "U" strips - and tail covering, the fighter was powered by two 525hp Gnome-Rhone 9AK nine-cylinder air-cooled radial engines. Armament consisted of two 76mm Kurchevski APK-4 recoilless weapons which were embodied in the tailbooms, the gun gases being discharged from their tails. Known unofficially as the Baumanskii Komsomolyets - in memory of the pre-revolutionary Communist after whom the district in which the TsAGI was situated was named - and officially as the I-12, the ANT-23 was first flown in late December 1931. Flight testing continued through early 1932, but, on 19 May, the port gun exploded, the tail-boom collapsing on touchdown. The aircraft was overweight and suffered substantially higher drag than had been calculated. Chernyshov and his team were developing a means of jettisoning the aft propeller to afford safe escape for the pilot in an emergency, but, at the beginning of 1933, the ANT-23 was abandoned.
 | A three-view drawing (1663 x 1095) |
| WEIGHTS |
| Take-off weight | 2400 kg | 5291 lb |
| DIMENSIONS |
| Wingspan | 15.60 m | 51 ft 2 in |
| Length | 9.50 m | 31 ft 2 in |
| Wing area | 30.00 m2 | 322.92 sq ft |
| PERFORMANCE |
| Max. speed | 300 km/h | 186 mph |
| wanshan, 20.06.2011 13:47 afford safe escape for the pilot in an emergency, but, at the beginning of 1933, the ANT-23 was abandoned. reply |
|
Do you have any comments?
|
| 
COMPANY
PROFILE
All the World's Rotorcraft
|