|
| The C1 (monoplace de chasse) requirement first issued
by the Service Technique Aeronautique in 1930 - when
it was finally conceded that the Jockey programme had
failed - and upgraded on 26 January 1931, resulted in no fewer than 10 designs being awarded prototype
contracts. These included two Morane-Saulnier proposals.
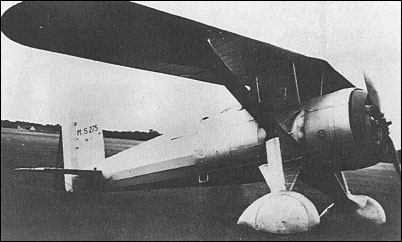
The first, the M.S.275, retained the classic parasol
monoplane configuration of preceding Morane-Saulnier
fighters and was flown in 1934. Powered by a
Gnome-Rhone 9Krse nine-cylinder radial rated at
600hp at 4000m and armed with two synchronised
7.7mm guns, the M.S.275 proved exceptionally
manoeuvrable and offered a very respectable performance.
It found little favour, however, owing to its
dated concept, development being discontinued, together
with that of the more innovative M.S.325, in favour of the more promising M.S.405 then in preliminary
design.
 | A three-view drawing (1278 x 860) |
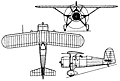
| WEIGHTS |
| Take-off weight | 1724 kg | 3801 lb |
| Empty weight | 1361 kg | 3001 lb |
| DIMENSIONS |
| Wingspan | 10.56 m | 35 ft 8 in |
| Length | 7.24 m | 24 ft 9 in |
| Height | 3.29 m | 11 ft 10 in |
| Wing area | 17.20 m2 | 185.14 sq ft |
| PERFORMANCE |
| Max. speed | 363 km/h | 226 mph |
| Ceiling | 10700 m | 35100 ft |
| Range | 1150 km | 715 miles |
|
Do you have any comments?
|
| 
COMPANY
PROFILE
All the World's Rotorcraft
|