|
Wight Quadruplane1916 |  |
| FIGHTER | Virtual Aircraft Museum / United Kingdom / Wight |
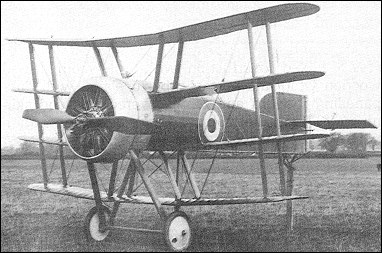 |
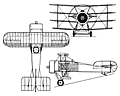
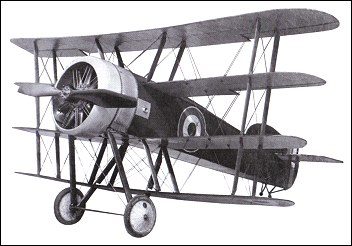
Confusingly, aircraft of original design produced by the J S White company bore the appellation Wight, to link them with the location of the works at Cowes on the Isle of Wight. The last of some eight types developed under the direction of Howard T Wright as chief designer was the only Wight aircraft in the fighter category. This was a quadruplane of most unusual layout, in which the fuselage filled the gap between the two middle wings, with the upper and lower mainplanes carried above and below it on struts. At first, single wide-chord struts were used for the cabane and for the single wing bays between the upper, mid-upper and mid-lower wings, all of which had ailerons. The bottom wing, of shorter span, was carried on pairs of struts under the fuselage, and from the mid lower wing. The main wheels were carried on single struts each side and were notched into the bottom wing, with which the axle was in line. Construction was of wood, with mixed fabric and plywood covering. The engine was a 110hp Clerget 9Z nine-cylinder rotary, but there is no record of the planned armament. Early flight testing, in mid-1916, led to a complete redesign and rebuild, by Howard T Wright and his team, with a fuselage of increased cross-section area and changed profile in side elevation, an enlarged tail unit and a new set of wings of varying chord. The original broad-chord struts gave way to pairs of narrow struts throughout and the undercarriage was lengthened. Possibly first tested at Martlesham Heath in February 1917, the Quadruplane acquired a third set of wings, with span progressively decreasing from top to bottom and ailerons on the two upper sets only. Further tests in July 1917 were unsatisfactory and the Quadruplane was written off in February 1918. FACTS AND FIGURES © The wing section was an original and very inefficient design by designer Howard Wright. There w camber at the leading and trailing edges but a flat middle section. © The Quadruplane's wingspan was less than the fuselage length, which by the time it appeared was the reverse of the established practice. © As first flown the wheels were recessed into the bottom wing and a large tailskid was needed to prevent the trailing edge scraping the ground. This was replaced by a more conventional arrangement.
|  All the World's Rotorcraft | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |

|