|
| There is no text information for this aircraft at the moment.
| ENGINE | 2 x 810hp Tiger VI |
| WEIGHTS |
| Take-off weight | 10940 kg | 24119 lb |
| DIMENSIONS |
| Wingspan | 26.82 m | 88 ft 0 in |
| Length | 24.61 m | 81 ft 9 in |
| Height | 5.94 m | 20 ft 6 in |
| Wing area | 121.51 m2 | 1307.92 sq ft |
| PERFORMANCE |
| Max. speed | 282 km/h | 175 mph |
| Ceiling | 6096 m | 20000 ft |
| Range | 1448 km | 900 miles |
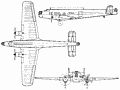 | A three-view drawing (900 x 677) |
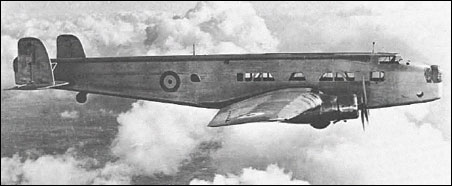
| lxbfYeaa, e-mail, 14.03.2024 05:56 20 reply | | Andres Erdös, e-mail, 05.09.2012 22:27 Specification C.26 /31 required a dual-purpose bomber /transport aircraft for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF), with the specification stressing the transport part of its role. The AW.23 was designed by John Lloyd, chief designer of Armstrong Whitworth to meet this specification, competing with the Handley Page HP.51 and the Bristol Bombay. The AW.23 was a low-wing twin-engine monoplane, powered by two Armstrong Siddeley Tiger engines. It had a fabric covered braced steel fuselage accommodating a large cabin to fulfill its primary transport role, but with room for internal bomb racks under the cabin floor. The aircraft's wings used a novel structure, patented by Armstrong Whitworth, which used a massive light alloy box-sparbraced internally with steel tubes. This structure was extremely strong but required a thick wing section, increasing drag. This wing structure was re-used in Armstrong Whitworth's Whitley bomber. The AW.23 was the first Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft to be fitted with a retractable undercarriage. A single prototype, K3585, was built first flying on 4 June 1935. Owing to its unreliable Tiger engines, its delivery to the RAF for testing was delayed, with the Bombay being declared the winner of the specification.
The prototype was given the civil registration G-AFRX in May 1939 being used for inflight refuelling development by Flight Refuelling Ltd who used it with the Short Empire flying boat. It was used in February 1940 for the world's first night refuelling experiments. It was destroyed in a German bombing raid on Ford airfield in June 1940.
General characteristics:
Crew: 4
Capacity: 24 troops
Length: 80 ft 9 in (24.62 m)
Wingspan: 88 ft 0 in (26.83 m)
Height: 19 ft 6 in (5.95 m)
Wing area: 1,308 ft² (122 m²)
Loaded weight: 24,100 lb (11,000 kg)
Powerplant: 2 × Armstrong Siddeley Tiger VI 14 cylinder Radial, 810 hp (604 kW) each
Performance:
Maximum speed: 140 kn (162 mph, 261 km /h) (TAS) at 6,500 ft
Range: 690 nmi (790 mi, 1,270 km) (estimated)
Service ceiling: 18,100 ft (5,520 m)
Wing loading: 18.4 lb /ft² (90.2 kg /m²)
Power /mass: 0.0672 hp /lb (0.11 W /kg)
Climb to 10,000 ft (3048m): 10 min 50 s
Armament:
Guns: Provision for single machine guns in nose and tail turrets
Bombs: provision for 2,000 lb (907 kg) bombs internally.
Wikipedia.com reply | | Klaatu83, e-mail, 18.12.2011 00:33 Designed as a military transport, similar to the Bristol Bombay. Although it was never produced in quantity, it formed the basis for the design of the Whitley bomber. reply | | daxiong, 20.06.2011 13:24 has a look of a plane more of the earlie 40's maybe with better engines it would have done better reply | |
| | Barry, 07.02.2011 14:13 You can see where the Whitley came from. reply | | Johned, e-mail, 14.07.2009 11:19 Looks a bit like a Fiat BR20 Cicogna reply | | james, e-mail, 01.01.2009 11:22 For the 1930's this has a look of a plane more of the earlie 40's maybe with better engines it would have done better reply |
|
Do you have any comments?
|
| 
COMPANY
PROFILE
All the World's Rotorcraft
|